In Our Time - Anaesthetics
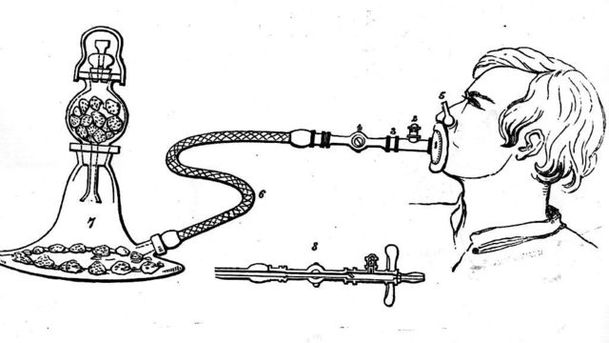
Melvyn Bragg and guests discuss the history of anaesthetics, from laughing gas in the 1790s to the discovery of “blessed chloroformâ€. Remembering his unsuccessful stint at Edinburgh Medical school Charles Darwin described the horrors of surgery before anaesthetics : "I attended the operating theatre and saw two very bad operations... but I rushed away before they were completed. Nor did I ever attend again, for hardly any inducement would have been strong enough to make me do so; this being long before the blessed days of chloroform. The two cases fairly haunted me for many a long year." The suffering Darwin witnessed is almost unimaginable. In the 19th Century, a simple fracture often led to amputation carried out on a conscious patient, whose senses would be dulled only by brandy or perhaps some morphine. Many patients died of shock. The properties of gases like nitrous oxide or “laughing gas†held out hope. The chemist Humphrey Davy in the 1790s described it as “highly pleasurable, thrillingâ€. He also noticed his toothache disappeared. But he failed to apply his observations and it wasn't until the 1840s that there was a major breakthrough in anaesthetics, when an enterprising dentist in Boston managed to anaesthetize a patient with ether. It became known as the “Yankee Dodgeâ€. Ether had its drawbacks and the search for a suitable alternative continued until chloroform was tried in 1847, winning many admirers including Queen Victoria, the first English royal to use it. So why did it take so long for inhaled gases to advance from providing merely recreational highs to providing an essential tool of humane surgery? What role did the development of the atomic bomb play in the development of anaesthetics? And how have society's changing attitudes to pain informed the debate? With David Wilkinson, Consultant Anaesthetist at St Bartholomew’s Hospital in London and President of the History of Anaesthesia Society; Stephanie Snow, Research Associate at the Centre for the History of Science, Technology & Medicine at the University of Manchester; Anne Hardy, Professor in the History of Modern Medicine at University College London